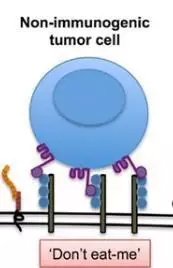
Since 1992, Yasumasa Ishida et al. have discovered PD-1 molecules in mouse hybridoma T cells [1]; by 2000, Gordon Freeman et al. discovered its first ligand, PD-L1 [2] In recent years, PD-1/PD-L1 antibody has achieved great results in the treatment of melanoma, colorectal cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, etc. [3]. Everyone's eyes are on the function of PD-1 to inhibit T cells. However, the PD-1 of "Tiaojiao" can be more than one point. History of PD-1 development Recently, Professor Irving Weissman of Stanford University found that the tumor mouse model and another immune cell in human tumors, macrophages, also express PD-1, and PD-1 also inhibits macrophage phagocytosis. Features. This means that PD-1 antibodies may trigger a double attack on tumors by activating T cells and macrophages! This finding will be important for the improvement and expansion of cancer PD-1/PD-L1 antibody therapy. Related research is published in the recent Nature [4]. Professor Irving Weissman About 10 years ago, scientists found in a variety of cancers, those patients with tumor cells expressing excessive PD-L1 have a poor prognosis [5]. Junzo Hamanishi also confirmed that PD-L1 expressed by tumor cells can directly act on killer T cells through PD-1 and inhibit its anticancer function [6]. PD-L1 is more like a "don't eat me" signal, which is expressed in tumor cells and releases this signal to the immune system to escape T cell attacks. At present, the use of PD-1 antibody or PD-L1 antibody in cancer treatment is to turn off this "don't eat me" signal to allow T cells to fight tumors [7]. Anesthesia and Breath Disposables Central Venous Catheter,Hemodialysis Catheter,Blood Pressure Transducer,Phripheral Inerted Central Catheter,Artery Compression Device Sampler,Infusion Pump Anesthesia Medical Co., Ltd. , https://www.medicaldiverse.com

Nature: Cancer cells cause macrophage indigestion