Anti-tumor drugs are one of the most active areas for the development of innovative drugs, and they are also areas where biomarkers can “make a big impactâ€. The heterogeneity of individuals in different tumor patients and the tissue heterogeneity of the same patient are great obstacles for the effective treatment of tumors. The use of biomarkers to distinguish cancerous species and determine drug response is the touchstone for precision medicine and anti-tumor drug development .
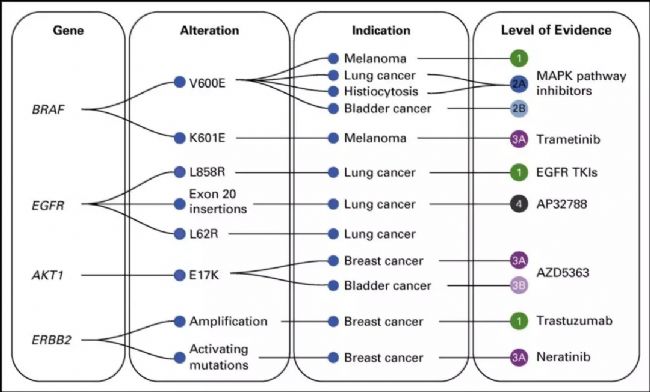
Figure 1. Application of tumor cell biomarkers 1
The discovery and development of biomarkers is challenging at an early stage. Determining a biomarker requires extensive analysis and validation, including research protocol design, population analysis, application correlation, etc., especially the high-throughput ensembles developed in recent years. Technology, methodological technology development, etc. have made the basic research of biomarkers into a high-speed development stage.
So the question is, what exactly is the biomarker for these (tumor tissue)?
First, biomarkers can be used for clinical testing, making these marker markers an important indicator of clinical testing and analysis.
However, not all biomarkers can be an indication for clinical prediction and diagnosis: the preclinical phase of the candidate biomarker needs to be analyzed and verified, ie the accuracy and reliability of the analyte and clinical validation of the patient sample is tested. . That is, the correlation and reliability of test results with clinical phenotypes or results of interest . After confirming the validity of the analysis, a biomarker analysis of the clinical phase is performed to confirm its performance in predicting or diagnosing the clinical phenotype or outcome of interest, consistent with the results of the discovery and validation phases. Analytical and clinically validated biomarkers generally include regulatory approvals, commercialization, coverage of health insurers, and inclusion of clinical practice guidelines in clinical applications.
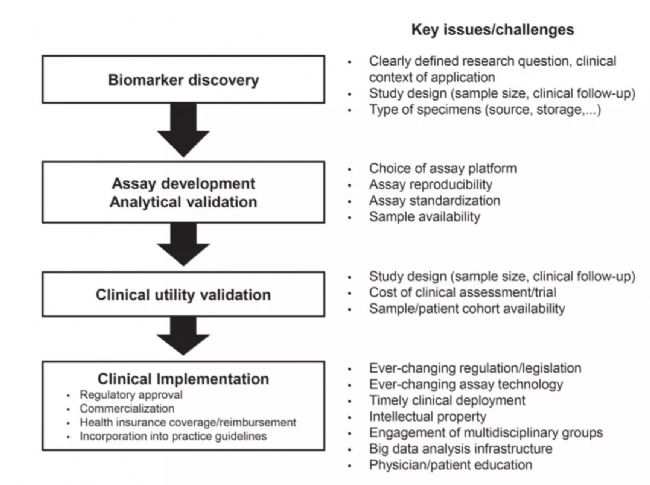
Figure 2. History of biomarkers 2
Biomarkers used to diagnose the development of tumors need to be above the detection limit, and are classified into predictive biomarkers, prognostic biomarkers, and diagnostic biomarkers according to their use.
Predictive biomarkers predict responses to specific therapeutic interventions, such as HER2 positive/activation, predicting breast cancer response to trastuzumab. Prognostic biomarkers may not be directly linked or triggered by specific treatment decisions, but their purpose is to inform future risk of clinical outcomes such as cancer recurrence or disease progression, such as using 21 gene recurrence scores to predict the overall survival rate of breast cancer. Diagnostic biomarkers are used to determine if a patient has a particular disease state, such as by detecting fecal cancer DNA, and diagnostic biomarkers have recently been used for the monitoring of colorectal cancer 3 .
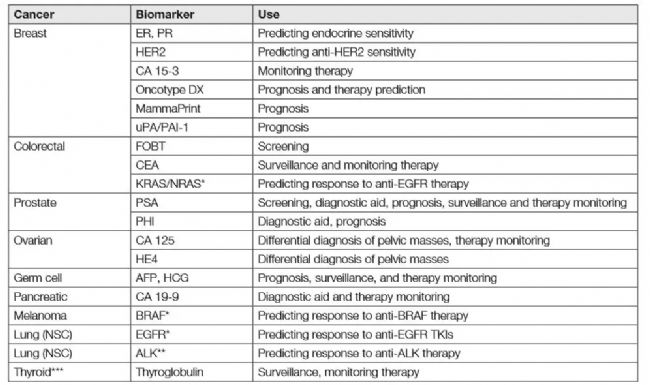
Table 1. Application of judgmental biomarker
Highly expressed and "human-free" biomarkers are the targets of biopharmaceutical research and development. The premise of precise treatment, the stronger the specificity, the better the accuracy of "ID card" pointing to a specific tumor . For example, in breast cancer patients with high expression of HER2 gene, trastuzumab treatment will control the development of tumor to some extent and prolong the progression-free survival of patients. Star targets include EGFR, BRAF, HER2, VEGFR, etc. The clinically widely used drugs are Erlotinib, Gefitinib, Bevacizumab, Cetuximab, and the like.
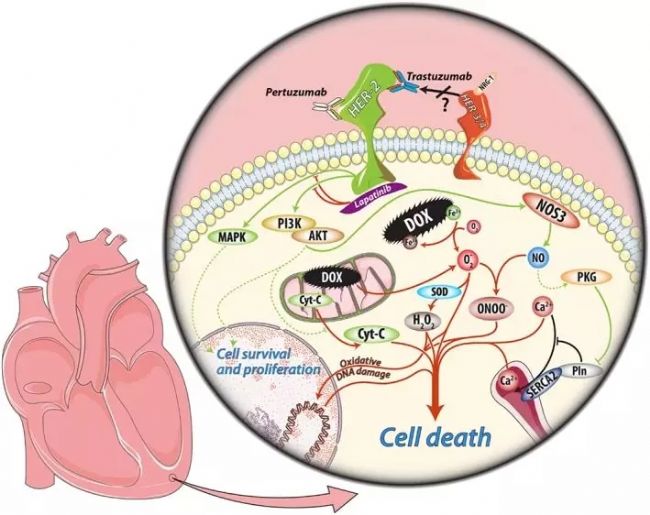
Figure 4. Anti-tumor mechanism of trastuzumab 4
The clinical application of monoclonal antibodies has become increasingly mature. By targeting tumor cells with biomarkers, by mobilizing the immune system's ADCC, ADCP and other mechanisms to kill tumors, accurate guidance on tumor cell killing can be achieved. The "specific" kills the new model of tumor cells!
However, in recent years, the hidden dangers of drug resistance have become increasingly prominent. The combination of two or more monoclonal antibodies or the study of bispecific antibodies is in full swing. Of the bispecific antibodies currently on the market, nearly one-third of the targets The focus on biomarkers of tumor cells, especially bispecific antibodies based on CD3 on T cells, has received increasing attention in recent years.
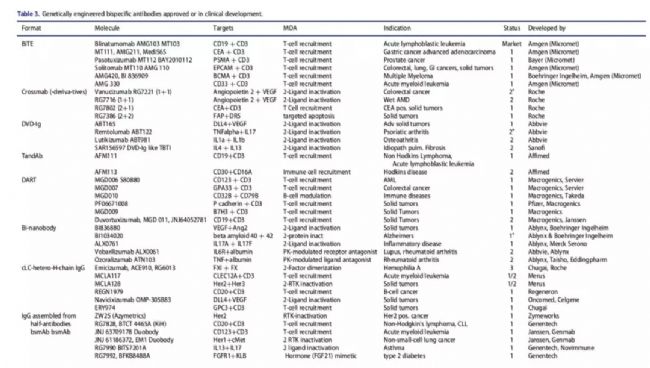
Table 2. Progress in the development of bispecific antibodies 5
Biographs has a variety of single/double/triple checkpoint mice, as well as a rich data CD3E humanized mouse model (and tumor marker protein humanized MC38 cell line) and B-NDG human immune system reconstruction. The mouse model can provide strong support for in vivo pharmacodynamic verification of CD3-based bispecific antibodies on T cells. For more information about our mouse model, please contact us!
references
1.Chakravarty D, Gao J, Phillips SM, Kundra R, Zhang H etc. OncoKB: A Precision Oncology Kno
Wledge Base, JCO Precis Oncol. 2017 Jul
2.Goossens N, Nakagawa S, Sun X, Hoshida Y. Cancer biomarker discovery and validation. Tran
Sl Cancer Res. 2015 Jun;4(3):256-269.
3.Klin. Clinical use of tumor biomarkers: An overview Biochem. Metab., 25 (46), 2017, No. 4, p.
157–161.
4.Nemeth B T, Varga Z V, Wu W J, et al. Trastuzumab cardiotoxicity: From clinical trials to exper
Imental studies[J]. British Journal of Pharmacology, 2016, 174(21).
5. Brinkmann U, Kontermann R E. The making of bispecific antibodies [J]. mAbs, 2017, 9(2): 182-
212.

Scan code to pay attention to the 100 Olympics map to learn more about consulting
5kw High Frequency Welding Machine
5Kw High Frequency Welding Machine,High Frequency Welder For Plastic Package,High Frequency Pvc Welding Machine,High Frequency Welding Machine For Tarpaulin
Wuxi DIZO Ultrasonic Technology Company , https://www.dizosonic.com