BACKGROUND INTRODUCTION Cardiovascular disease is the highest mortality rate in many countries. Hyperlipidemia is the most important factor in accelerating atherosclerosis and increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease. Because of the considerable side effects of hypolipidemic drugs, there is an urgent need to reduce blood lipids through dietary interventions without side effects. Soy products are rich in high-quality protein and isoflavones that help improve human health. Many studies have confirmed that soy protein not only significantly lowers serum total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c) concentrations, but also significantly increases high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c). concentration. Among them, isoflavones play an important role in reducing TC and LDL-c levels and regulating apolipoproteins and antioxidants. There are many traditional fermented soy products such as soy sauce, miso and natto. Studies have shown that this fermented soy product has higher biological activity and is more conducive to human body absorption. Soy products fermented by lactic acid bacteria can significantly reduce hyperlipidemia and help reduce the risk of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. In 2017, Zhejiang University Chunmei Yang and others published an article entitled "Antioxidant and hypolipidemic effects of soymilk fermented via Lactococcus acidophilus MF204" in "Food & Function" magazine (IF=3.289, Agriculture and Forestry 2 District). Main method used METHODS 1. SD rat model establishment; 2. TC, TG, LDL-c, HDL-c detection; 3. SOD, GSH-Px, T-AOC detection; 4. HPLC: High performance liquid chromatography is a chromatographic method in which a specified mobile phase is pumped into a column using a high pressure infusion pump to separate and measure the sample. It is suitable for samples which can be made into a solution after dissolution. It is not limited by the volatility and thermal stability of the sample and has a wide range of uses. ABSTRACT Studies have shown that fermentation can increase the biological activity and absorption rate of soy products. Fermented soy products can reduce hyperlipidemia and reduce the risk of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects and mechanisms of soymilk fermented by acidophilus Lactococcus on blood lipids and antioxidant enzyme activities in rats fed with high fat diet. Sixty rats were randomly divided into 6 groups: normal control group (NC), high fat control group (HFC), positive control group (cholestyramine, PC), acidophilus group (LA), unfermented soymilk group. (SM) and fermented soymilk (FSM). The NC group was fed a basic diet while the other groups were fed a high-fat diet. After 6 weeks of feeding, the rats were sacrificed, and blood and liver were separately collected to measure lipid concentration and antioxidant enzyme activity. The results showed that fermented soymilk could regulate lipid levels, restore HDL-c and TG to normal levels, and found that LDL-c levels were significantly lower than those in positive control (PC) rats treated with hypolipidemic drugs. More importantly, fermented soymilk not only significantly reduced the arteriosclerosis index and coronary artery risk index, but also improved the antioxidant capacity of hyperlipidemic rats. This may be related to an increase in aglucone isoflavones in fermented soymilk. In conclusion, soymilk fermented by L. acidophilus reduces the risk of arteriosclerosis and coronary heart disease by regulating lipid levels and improving the antioxidant capacity of hyperlipidemic rats. O2 Cylinder,Medical Liquid Oxygen Tank,Blue Medical Liquid Oxygen Tank,60L Oxygen Cylinder JIANGSU NEW FIRE FIGHTING TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD , https://www.newayfire.com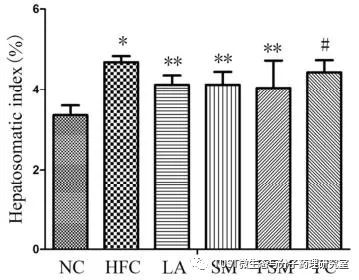
Food & Funct: Antioxidant and hypolipidemic effects of Lactococcus lactis fermented soymilk
Next Article
Grape post-harvest management technical points
Prev Article
Houttuynia plantation management technology