Release date: 2017-03-14 Exercise is good for both physical and mental health, which is already a common topic. Numerous studies have shown that regular exercise can delay aging, strengthen the immune system, improve cognitive ability, improve sleep, and prolong life... But how does physical activity achieve this process at the cellular level? Recently, a study published in the journal Cell Metabolism revealed the mechanisms behind the benefits of exercise. Exercise—especially high-intensity interval training (HIIT) in aerobic exercise, such as cycling and walking, can promote cells to produce more protein for mitochondria and ribosomes, effectively delaying aging at the cellular level. The senior author of the study was Dr. Sreekumaran Nair, a diabetes researcher at the Mayo Clinic. He said, "In the aspect of delaying aging, the benefits of exercise are irreplaceable, and the benefits we observe cannot be accomplished by any drugs." The study investigated 36 men and 36 women and divided them into two age groups: “young†(aged between 18 and 30 years old) and “elderly†(aged between 65 and 80 years old). The researchers asked these participants to do three exercise programs: High-intensity intermittent cycling training Strength training by weightlifting Interval training and strength training combination The researchers performed biopsy from the thigh muscles of volunteers and compared their molecular composition with the sedentary control group. In addition, the researchers also assessed lean muscle mass and insulin sensitivity. The team found that although strength training is helpful in building muscle mass, high-intensity interval training has the greatest benefit at the cellular level, especially for mitochondria. Intermittent training by young volunteers showed a 49% increase in mitochondrial capacity, compared with 69% in the elderly group. High-intensity bicycle training effectively reverses age-related declines in mitochondrial function. Exercise, mitochondria and aging Intracellular power plants - The main function of mitochondria is to produce the energy substance ATP. As we age, the ability of mitochondria to produce energy is gradually diminished. By comparing the proteomics and RNA sequencing data of the exercise group, the team found that exercise promotes the production of more RNA copies of genes encoding mitochondrial proteins and muscle growth-related proteins in cells. The high-intensity cycling program also promotes the protein synthesis machine, ribosome regeneration. It enhances the ability to construct mitochondrial proteins, which explains the effects of increased mitochondrial function and muscle mass. Increase protein to slow down aging It is important to strengthen protein production through physical activity. Muscle cells, like brain and heart cells, do not divide often. This means that as they age, their function gradually declines. As Dr. Nair said: “Unlike the liver, muscles are not easily regenerated, and cells accumulate a lot of damage. If exercise can restore or minimize the deterioration of ribosomes and mitochondria in muscle cells, then similarities should exist in other tissues. mechanism." In addition to increasing mitochondrial function, interval training also increases insulin sensitivity in participants and reduces the risk of diabetes. However, this type of exercise is less effective in improving muscle strength. Although the study did not focus on recommendations for duration of exercise or type of exercise, Dr. Nair said: "If people have to choose a sport, I recommend high-intensity interval training, but I think if they can do it for 3-4 days. Interval training, and then a few days of strength training, should be more beneficial. However, of course, any exercise is better than no exercise. The study clearly illustrates how exercise increases the yield of specific organelles. This relationship may play a key role in slowing down cellular aging. Dr. Nair and his team plan to further study the benefits of exercise at the cellular level in other tissue types. In the future, these findings may help reduce the impact of aging. But for now, strenuous exercise is still the most effective way to promote health. As Dr. Nair said: “There is a large amount of basic scientific data to support exercise that is essential to prevent or delay aging, which cannot be replaced.†Reference materials: Enhanced Protein Translation Underlies Improved Metabolic and Physical Adaptations to Different Exercise Training Modes in Young and Old Humans Exercise prevents cellular aging by boosting mitochondria Source: Bio-Exploration
China Vegetable Powder,Freeze Dried Kale Powder supplier & manufacturer, offer low price, high quality Kale Powder,Celery Seed Powder, etc.
Healthway was founded in 2009 who is an professional manufacture that can produce herb extract and super food supplement. We had passed FDA certificate and ISO 9001 .Welcome any inquiry and question on our featured products via Alibaba.
Vegetable Powder,Freeze Dried Kale Powder,Kale Powder,Celery Seed Powder Xi'an Healthway Biotech Co.,Ltd , http://www.xahealthway.com
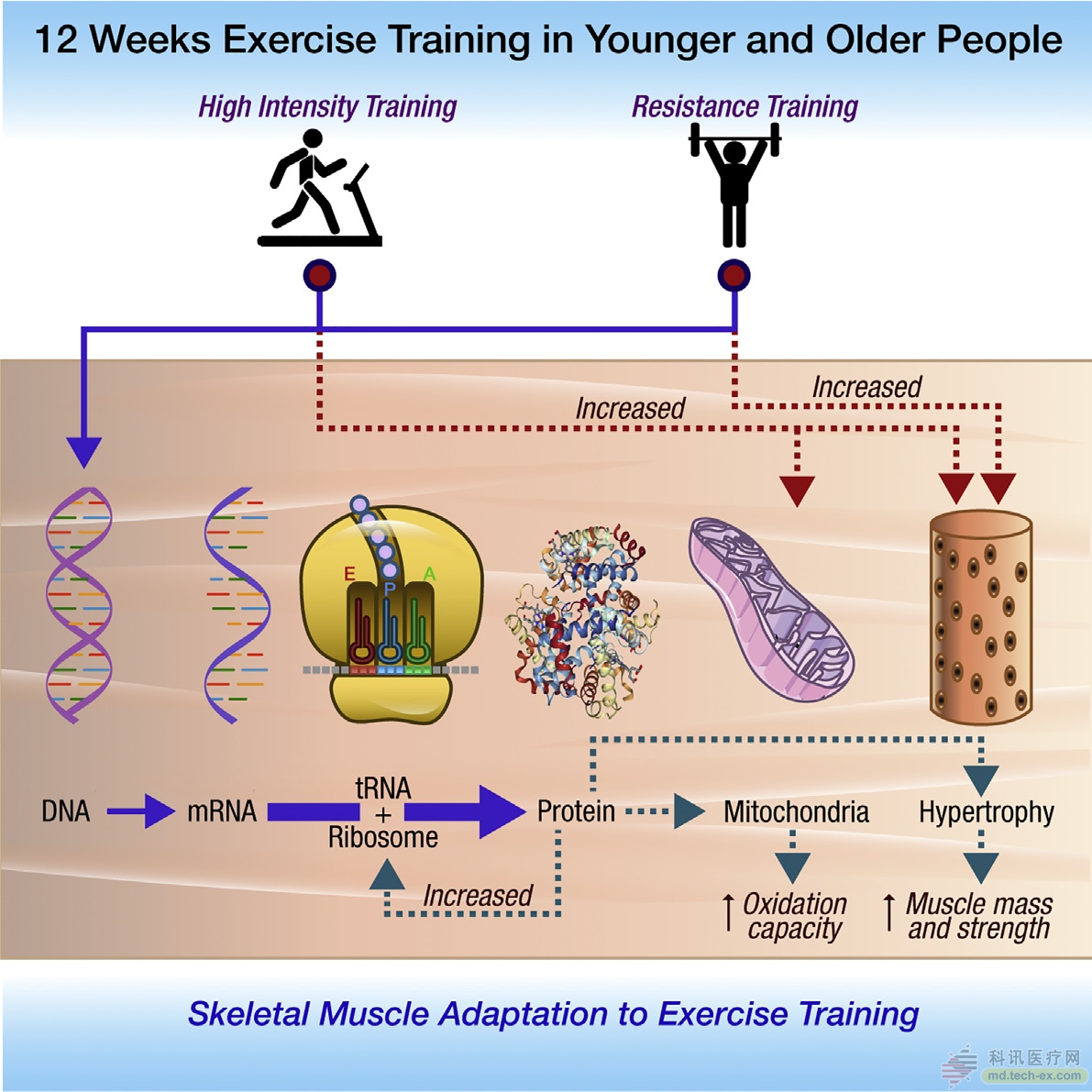
CELL METAB: Exercise delays aging, so which exercise works best?
Next Article
How to prevent insect pests in winter