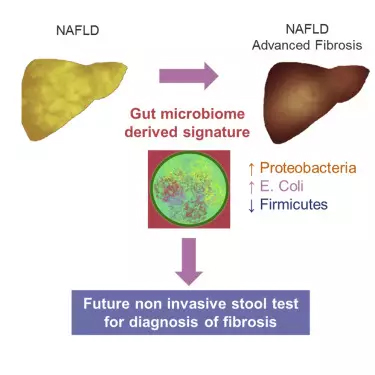
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a clinical pathological syndrome with a history of liver histology similar to alcoholic liver disease but no history of excessive drinking. The disease can eventually lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer, but the condition is often developed in the late stages. Also, the diagnosis requires an invasive liver biopsy. For the early and non-invasive detection of NAFLD, the University of California, San Diego Medical University NAFLD Research Center, Human Longevity Research Institute and J. Researchers at the Craig Venter Institute have found that patient stool samples or gut microbiota may be used to predict advanced NAFLD with an accuracy of 88% to 94%. The proof-of-concept study involving 135 participants was published on May 2nd at Cell Metabolism. "About 100 million adults and children in the United States may have NAFLD, but it is still very difficult to accurately diagnose patients at risk of or at risk," said Professor Rohit Loomba, the lead author of the study. There are 50 new NAFLD drugs in development, including five drugs that will be approved for use in the next two years. If we can better diagnose the disease, we will recruit more appropriate patients in these experiments. Finally, it is better to prevent and treat the disease." The exact cause of NAFLD remains unknown, but diet and genetics play an important role. More than 50% of obese people also have NAFLD. In recent years, there is growing evidence that gut microbiota may affect our risk of obesity. Loomba and the team began to wonder whether the gut microbiota could also be associated with obesity-related liver disease. If so, can you diagnose the state of NAFLD by detecting fecal microbes? Differences in microbial components of feces in early and late NAFLD To answer these questions, Loomba and the team investigated two different groups of patients. The first group included 86 patients with NAFLD diagnosed by biopsy. Of these, 72 were mild/moderate NAFLD and 14 were advanced. Bacterial distribution and relative abundance were determined by sequencing the microbial genes extracted from each participant's stool samples. The researchers found that 37 bacterial species differentiated mild/moderate NAFLD from advanced disease, and this method can predict which patients develop advanced disease with an accuracy of 93.6%. The team further validated the findings through a second study that included 16 patients with advanced NAFLD and 33 healthy controls as controls. In this experiment, the researchers found nine bacteria, and the relative amount of the bacteria allowed the researchers to distinguish between NAFLD patients and healthy volunteers with an accuracy of 88%. Seven of these bacteria overlap with the 37 found in the previous set of experiments. Image source: original research Herbal Extract According to different extraction methods: the volatile oil, oil, extract, fluid extract, dry extract, active components and active parts obtained from plants for preparation production are all extracts. Herbal Extract,Herbal Extract Powder,Herbs Extract Shaanxi Zhongyi Kangjian Biotechnology Co.,Ltd , https://www.zhongyibiology.com
Herbal extracts were classified according to ingredients: glycosides, acids, polyphenols, polysaccharides, terpenoids, flavonoids, alkaloids, etc. Active Ingredient : natural single ingredient extracted from plants and other substances, the content of the single ingredient should account for more than 90% of the total extract.
Herbal extracts are classified according to their efficacy:Immune-boosting extract,Antialcoholic Liver Extract,Sleep Improving Extract,Purgative Extract,Treat Pharyngeal Extract.
According to the characteristics of the final product, it can be divided into oil, liquid, powder, lens and so on.
Cell: Fecal microbes are expected to detect early fatty liver and cirrhosis
Next Article
Feeding method for broiler chicken